

- September 30, 2023
- 4:50 pm
- No Comments
A Comprehensive Guide to CRM Analytics (2023)
CRM analytics, a multifaceted tool, leverages data-driven insights to boost customer engagement, optimize operations, and drive revenue growth. In this blog, we will explore the basis of CRM analytics, its diverse applications, and how it can revolutionize your customer relationships.
1. Understanding CRM Analytics
Understanding CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Analytics is the foundation upon which businesses can unlock valuable insights into their customer base and operations.
CRM analytics is a data-driven approach that involves the systematic analysis of customer data and interactions to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and trends. It goes beyond merely collecting data; it involves extracting meaningful information to make informed decisions.

CRM analytics encompasses various aspects, including customer segmentation, sales forecasting, customer lifetime value (CLV) calculations, and churn rate analysis. By segmenting customers based on their attributes and behavior, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts and product offerings to specific groups, thereby increasing customer engagement and satisfaction.
Furthermore, analytical CRM aids in predicting future trends and customer behavior, allowing businesses to make proactive decisions. Understanding CRM analytics is not just about collecting data; it’s about harnessing the power of data to improve customer relationships, optimize operations, and ultimately drive growth.
2. Benefits of CRM Analytics
2.1 Enhanced Customer Understanding
CRM analytics offers profound insights into customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. By analyzing data, businesses can segment their customer base effectively, identify their most valuable customers, and tailor marketing strategies to specific demographics.
2.2 Improved Decision-Making
CRM analytics serves as a reliable compass for decision-makers within an organization. By harnessing the power of data, businesses can make decisions that are rooted in empirical evidence rather than gut feeling. This data-driven approach extends to various facets of the business, including product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns.
Decision-makers can use analytical CRM to identify emerging trends, customer preferences, and market opportunities. As a result, businesses can allocate resources more effectively and optimize their processes, leading to increased profitability and a competitive edge in the market.
2.3 Increased Sales and Revenue
CRM analytics identifies cross-selling and upselling opportunities, helping businesses generate additional revenue from existing customers. By analyzing historical data, sales teams can focus on leads with the highest conversion potential, resulting in a more efficient sales process.
2.4 Enhanced Customer Service
Exceptional customer service is a cornerstone of successful businesses, and CRM analytics plays a pivotal role in achieving it. Armed with this information, businesses can take a proactive approach to customer service.
Moreover, companies can predict customer needs, anticipate potential issues, and even resolve problems before customers are aware of them. This level of responsiveness and efficiency not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces churn rates as customers are less likely to switch to competitors when their needs are consistently met.
2.5 Efficient Resource Utilization
By analyzing data on customer interactions, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently. This includes optimizing staffing levels, inventory management, and marketing budgets. Analytical CRM ensures that resources are utilized where they are most needed, reducing wastage and increasing operational efficiency.
3. Key CRM Analytics Metrics to measure CRM performance
3.1 Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer Acquisition Cost assesses the cost incurred to acquire a new customer. Calculated by dividing the total marketing and sales expenses by the number of new customers gained within a specific period, CAC helps businesses do CRM evaluation the efficiency of their marketing and sales efforts. A lower CAC suggests a more cost-effective acquisition strategy, while a higher one may indicate the need for optimization.

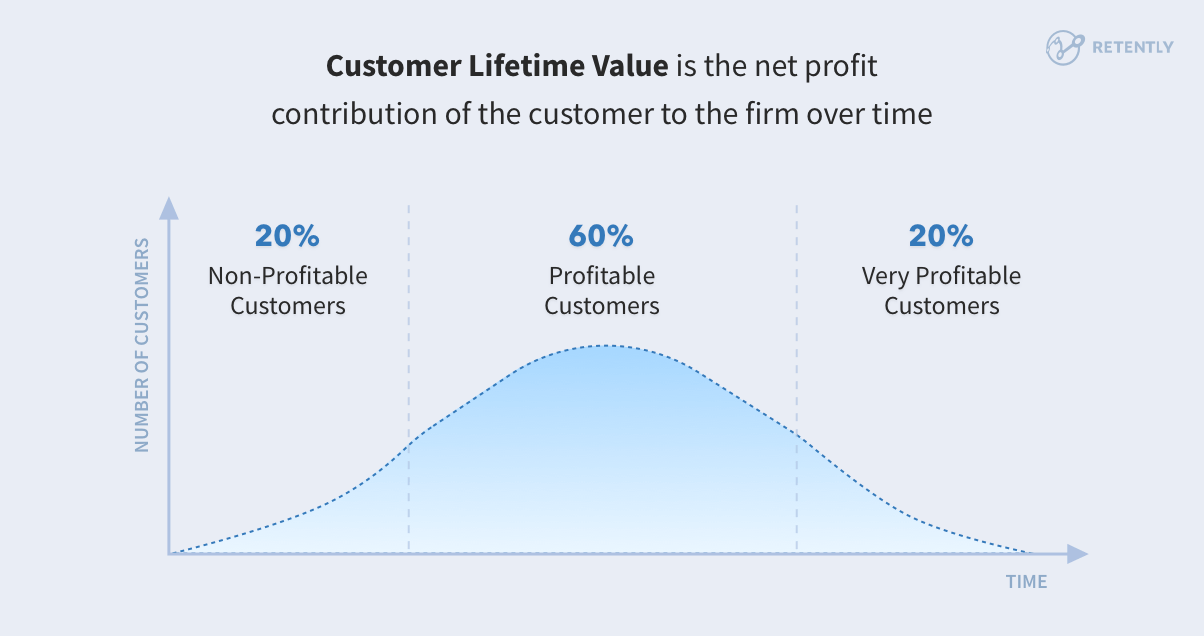
3.2 Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer Lifetime Value measures the total revenue a business expects to earn from a customer throughout their entire relationship. By predicting the future value of a customer based on historical data, businesses can prioritize high-CLV customers, tailor marketing strategies, and make informed decisions on retention efforts.
3.3 Churn Rate
Churn Rate quantifies the percentage of customers who stop using a company’s products or services during a given period. A high churn rate indicates a problem with customer retention and calls for corrective measures. By analyzing the reasons for churn, businesses can identify pain points and improve customer experiences.

3.4 Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
CSAT is a direct measure of customer satisfaction based on surveys and feedback. It quantifies how satisfied customers are with a product or service. A high CSAT score indicates high satisfaction levels, while a low score signals dissatisfaction. Tracking CSAT helps identify areas for improvement and gauge the success of customer-centric initiatives.

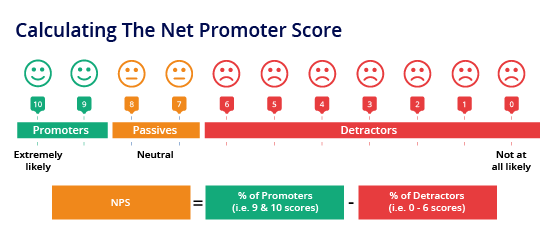
3.5 Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score measures customer loyalty and advocacy. It asks customers how likely they are to recommend a company’s product or service to others. Promoters (those who score 9-10) are advocates, while detractors (those who score 0-6) are potential risks. Calculating the NPS helps gauge overall customer sentiment and identify opportunities to turn customers into brand ambassadors.
3.6 Customer Retention Rate
Customer Retention Rate is one of the marketing crm metrics that measures the percentage of customers who continue to do business with a company over time. A high retention rate signifies customer loyalty and ongoing value. Analyzing this metric helps uncover strategies to improve retention and reduce churn, ultimately leading to increased revenue and profitability.

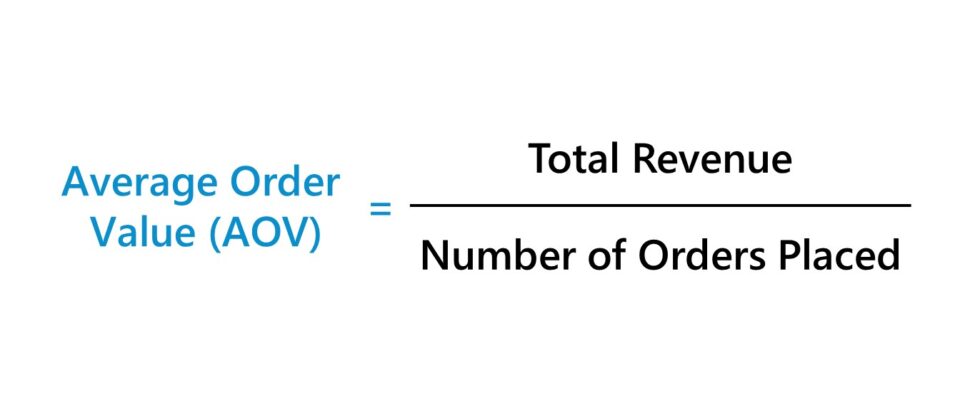
3.7 Average Order Value (AOV)
Average Order Value is a crucial metric for e-commerce businesses. It calculates the average amount customers spend per transaction. A rising AOV can indicate successful upselling or cross-selling strategies, while a declining AOV may signal a need to adjust pricing or promotional tactics.
3.8 Sales Conversion Rate
Sales Conversion Rate measures the percentage of leads or visitors who become paying customers. This metric helps businesses assess the effectiveness of their sales funnel. By analyzing conversion rates at different stages, companies can identify bottlenecks and optimize their sales process to boost revenue.
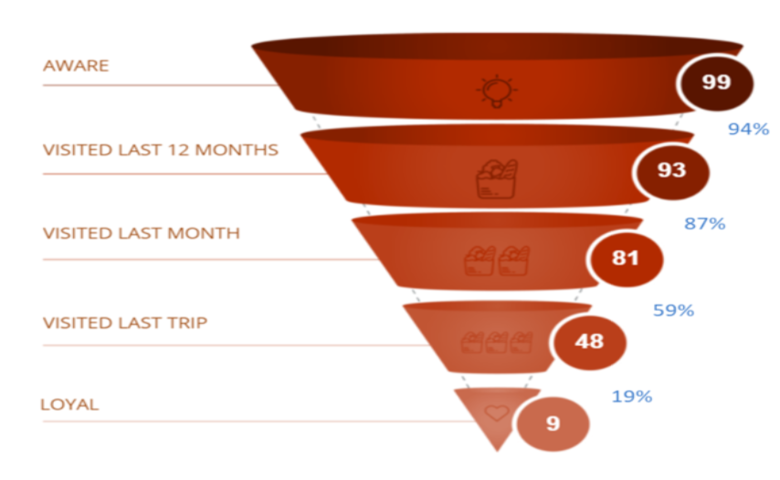
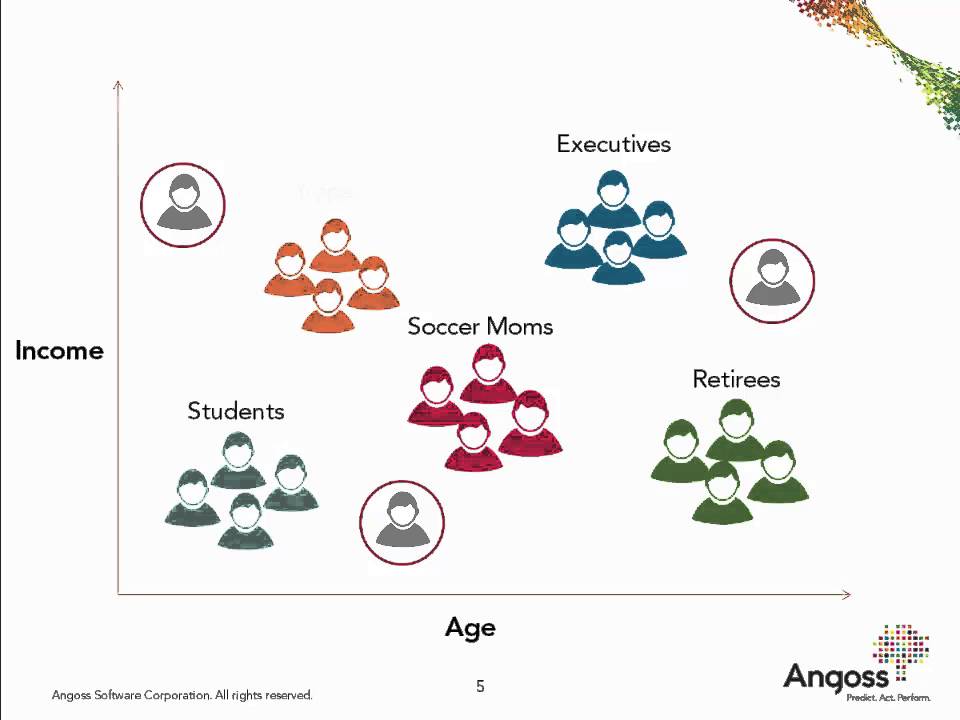
3.9 Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation involves dividing the customer base into distinct groups based on characteristics or behavior. By analyzing these segments individually, businesses can tailor marketing efforts, products, and services to better meet the unique needs of each group, leading to improved customer engagement and higher sales.
3.10 Lead Velocity Rate (LVR)
Lead Velocity Rate measures the rate at which new leads are entering the sales funnel. A consistent increase in LVR indicates a healthy flow of potential customers and a robust sales pipeline. This metric is particularly valuable for businesses looking to scale and grow their customer base.

4. Data Collection and Integration
Step 1: Identify Data Sources: Begin by identifying all potential data sources within your organization. These can include customer interactions, website analytics, sales records, social media, customer feedback, and more. The goal is to capture a comprehensive view of your customers and their behavior.
Step 2: Centralize Data Storage: Create a centralized repository or database where all collected data is stored. This ensures that data is easily accessible, reducing the risk of siloed information and making it simpler to perform cross-channel analysis.
Step 3: Automate Data Collection: Leverage automation tools and software to streamline data collection processes. For instance, use web analytics tools to track website visits, email marketing platforms to capture customer interactions, and CRM systems to record sales and customer details. Automation not only saves time but also minimizes manual errors.
Step 4: Define Data Quality Standards: Establish clear data quality standards and protocols. Data should be accurate, complete, consistent, and up-to-date. Implement data validation rules to ensure that new data adheres to these standards upon entry.
Step 5: Data Cleaning and Transformation: Regularly clean and transform data to maintain its quality. This involves removing duplicate entries, correcting errors, and standardizing formats. Data cleansing tools can be immensely helpful in this regard.
Step 6: Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize data security and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). Implement encryption, access controls, and audit trails to protect sensitive customer data.
Step 7: API Integration: Integrate various software systems and applications through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to facilitate data sharing and synchronization. This ensures that data is consistently updated across all platforms.
Step 8: Data Validation and Testing: Implement data validation checks and conduct regular testing to identify anomalies or data inconsistencies. This proactive approach helps in detecting and rectifying issues before they impact analysis.
Step 9: Data Governance: Establish a data governance framework that outlines roles, responsibilities, and processes for data management. A data governance committee can oversee data policies and practices.
Step 10: Data Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of data sources, collection methods, and transformations. This documentation is valuable for future reference and audits.
5. Customer Segmentation and Targeting
Customer segmentation and targeting are foundational strategies in marketing, and CRM analytics plays a pivotal role in making these practices more effective. Here’s how CRM analytics can be used to segment customers based on behavior, demographics, and preferences
5.1 Behavior-Based Segmentation
CRM analytics allows businesses to segment customers based on their interactions and behavior. By analyzing data on website visits, product purchases, email engagement, and more, companies can categorize customers into groups with similar behaviors.
For example, they can identify frequent shoppers, occasional buyers, or customers who abandoned their carts. This information helps tailor marketing messages and product recommendations to each segment, increasing the likelihood of conversions.
5.2 Demographic Segmentation
Demographic information such as age, gender, income, location, and occupation is a crucial aspect of customer segmentation. Customer analytics in CRM enables organizations to collect and analyze this data to create customer profiles based on demographics.
For instance, a clothing retailer might target different age groups with specific fashion styles or offer location-based promotions to customers in particular regions. This level of personalization resonates with customers and enhances engagement.

5.3 Preference-Based Segmentation
Preferences, including product preferences, communication channel preferences, and content preferences, can be discerned through CRM analytics. By tracking customer responses to email campaigns, surveys, or content consumption patterns, businesses can segment customers according to their preferences.
For instance, an e-commerce platform might send fashion updates to customers interested in clothing and gadget news to tech enthusiasts. This not only enhances engagement but also prevents message fatigue.

5.4 Predictive Segmentation
Customer analytics in CRM also allows for predictive segmentation, wherein machine learning models analyze historical data to predict future behaviors or preferences. For example, predictive analytics can identify customers who are likely to make a purchase soon or those at risk of churning. Businesses can then create targeted marketing campaigns to encourage purchases or retain at-risk customers.

5.5 Lifecycle Segmentation
CRM analytics can segment customers based on their lifecycle stage with the company. This includes new customers, loyal customers, and dormant customers. Each group may require different engagement strategies.
For example, new customers might benefit from onboarding emails, while loyal customers could receive exclusive offers and rewards.
5.6 Custom Segmentation Criteria
CRM analytics provides the flexibility to create custom segmentation criteria specific to a business’s unique needs. Whether it’s segmenting customers based on their purchase history, subscription status, or even social media interactions, Customer analytics in CRM can accommodate diverse segmentation criteria.
6. Predictive Analytics in CRM
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool within Customer Relationship Management (CRM) that leverages historical customer data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future customer behaviors, preferences, and trends. Here’s a closer look at how predictive analytics transforms CRM.
6.1 Anticipating Customer Behavior
Predictive analytics helps businesses forecast future customer actions, including purchase behavior, product preferences, and churn likelihood, enabling proactive and personalized marketing.
6.2 Personalized Customer Experiences
Through the analysis of historical data and predictive modeling, businesses can create highly personalized interactions with customers. Predictive analytics helps in understanding and meeting individual customer needs, leading to increased engagement and satisfaction.
6.3 Sales and Revenue Optimization
Predictive analytics identifies high-value leads and predicts conversion probabilities. This enables sales teams to prioritize their efforts effectively, leading to improved sales efficiency and revenue generation.
6.4 Enhanced Customer Retention
Predictive analytics can identify customers at risk of churning. By intervening with targeted retention efforts, such as loyalty programs or personalized outreach, businesses can prevent customer attrition and strengthen customer relationships.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, the strategic use of CRM analytics has emerged as an indispensable asset for businesses aspiring to thrive.
Surfline Media stands as your trusted partner, offering top-tier CRM services at an affordable price, ensuring that you can harness the true potential of CRM analytics without breaking the bank. It’s time to elevate your customer relations, optimize your operations, and drive unprecedented growth. Choose quality, choose Surfline Media, and unlock the transformative power of Customer analytics in CRM for your business.
_______________________

Surfline Media – Automate to Elevate
Our website: https://surflinemedia.com/
Contact us: https://surflinemedia.com/contact-us/
Phone number: +1 323-741-4482
Email: [email protected]






